footnote*Vanguard average mutual fund expense ratio: 0.10%. Industry average mutual fund expense ratio: 0.63%. All averages are asset-weighted. Industry averages exclude Vanguard. Sources: Vanguard and Morningstar, Inc., as of December 31, 2019.
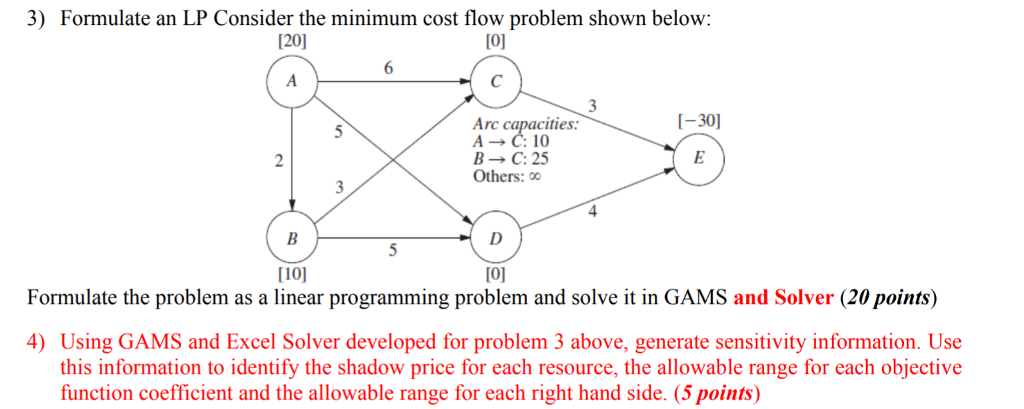
- 9) For a minimum cost flow problem to have a feasible solution, which of the following must be true? A) There is the same number of supply nodes and demand nodes. B) There is only one supply node and one demand n C) There is an equal amount of supply and demand.
- Positioni + 2 or positioni - 2 with cost = 0. Positioni + 1 or positioni - 1 with cost = 1. Return the minimum cost needed to move all the chips to the same position. Example 1: Input: position = 1,2,3 Output: 1 Explanation: First step: Move the chip at position 3 to position 1 with cost = 0. Second step: Move the chip at position 2.
- The minimum efficient scale (MES) is the lowest point on a cost curve at which a company can produce its product at a competitive price. At the MES point, the company can achieve the economies of.
footnote**Commission-free trading of Vanguard ETFs applies to trades placed both online and by phone. Commission-free trading of non-Vanguard ETFs excludes leveraged and inverse ETFs and applies only to trades placed online; most clients will pay a commission to buy or sell non-Vanguard ETFs by phone. Commission-free trading of non-Vanguard ETFs also excludes 401(k) participants using the Self-Directed Brokerage Option; see your plan's current commission schedule. Vanguard Brokerage reserves the right to change the non-Vanguard ETFs included in these offers at any time. All ETFs are subject to management fees and expenses; refer to each ETF's prospectus for more information. Account service fees may also apply. All ETF sales are subject to a securities transaction fee. See the Vanguard Brokerage Services commission and fee schedules for limits.
Proving what it means to put value first. At Fidelity, we're committed to giving you value you can't find anywhere else. That's why we introduced zero expense ratio index mutual funds. 2 We also offer zero minimum investment Fidelity Mutual Funds, no minimums to open an account, 3 no account fees for retail brokerage accounts, and 24/7 live customer service — now that's value.
footnote***Some funds have higher minimums to protect the funds from short-term trading activity. Fund-specific details are provided in each fund profile.
You must buy and sell Vanguard ETF Shares through Vanguard Brokerage Services (we offer them commission-free) or through another broker (which may charge commissions). Vanguard ETF Shares aren't redeemable directly with the issuing fund other than in very large aggregations worth millions of dollars. ETFs are subject to market volatility. When buying or selling an ETF, you'll pay or receive the current market price, which may be more or less than net asset value.

Investments in Target Retirement Funds are subject to the risks of their underlying funds. The year in the fund name refers to the approximate year (the 'target date') when an investor in the fund would retire and leave the workforce. The fund will gradually shift its emphasis from more aggressive investments to more conservative ones based on its target date. An investment in a Target Retirement Fund is not guaranteed at any time, including on or after the target date.

All investing is subject to risk, including the possible loss of the money you invest.
Definition: The Least Cost Method is another method used to obtain the initial feasible solution for the transportation problem. Here, the allocation begins with the cell which has the minimum cost. The lower cost cells are chosen over the higher-cost cell with the objective to have the least cost of transportation.
The Least Cost Method is considered to produce more optimal results than the North-west Corner because it considers the shipping cost while making the allocation, whereas the North-West corner method only considers the availability and supply requirement and allocation begin with the extreme left corner, irrespective of the shipping cost.
Let’s understand the concept of Least Cost method through a problem given below:
In the given matrix, the supply of each source A, B, C is given Viz. 50units, 40 units, and 60 units respectively. The weekly demand for three retailers D, E, F i.e. 20 units, 95 units and 35 units is given respectively. The shipping cost is given for all the routes.
The minimum transportation cost can be obtained by following the steps given below:
- The minimum cost in the matrix is Rs 3, but there is a tie in the cell BF, and CD, now the question arises in which cell we shall allocate. Generally, the cost where maximum quantity can be assigned should be chosen to obtain the better initial solution. Therefore, 35 units shall be assigned to the cell BF. With this, the demand for retailer F gets fulfilled, and only 5 units are left with the source B.
- Again the minimum cost in the matrix is Rs 3. Therefore, 20 units shall be assigned to the cell CD. With this, the demand of retailer D gets fulfilled. Only 40 units are left with the source C.
- The next minimum cost is Rs 4, but however, the demand for F is completed, we will move to the next minimum cost which is 5. Again, the demand of D is completed. The next minimum cost is 6, and there is a tie between three cells. But however, no units can be assigned to the cells BD and CF as the demand for both the retailers D and F are saturated. So, we shall assign 5 units to Cell BE. With this, the supply of source B gets saturated.
- The next minimum cost is 8, assign 50 units to the cell AE. The supply of source A gets saturated.
- The next minimum cost is Rs 9; we shall assign 40 units to the cell CE. With his both the demand and supply of all the sources and origins gets saturated.
Minimum Cost Model
The total cost can be calculated by multiplying the assigned quantity with the concerned cost of the cell. Therefore,
Total Cost = 50*8 + 5*6 + 35*3 +20*3 +40*9 = Rs 955.
Minimum Cost Tree
Note: The supply and demand should be equal and in case supply are more, the dummy source is added in the table with demand being equal to the difference between supply and demand, and the cost remains zero. Similarly, in case the demand is more than supply, then dummy destination or origin is added to the table with the supply equal to the difference in quantity demanded and supplied and the cost being zero.
Minimum Cost Of Living
Related terms:
